Technology has had a significant impact on the way students learn today. It has provided new tools and resources for students to access information and resources, as well as new ways for students to interact with teachers and classmates. Some examples of technology that have changed the way students learn include:
Online learning platforms, such as Blackboard, Canvas, and Google Classroom, allow students to access course materials, submit assignments, and communicate with teachers and classmates online.
Educational software, such as Khan Academy, Duolingo, and Codecademy, provides interactive, self-paced lessons on various subjects.
Learning management systems (LMS), allow teachers to create and manage online course content and track student progress.
Digital textbooks can be updated more quickly and are often cheaper than traditional textbooks.
Virtual and augmented reality, can provide immersive learning experiences and allow students to visualize complex concepts.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning can give personalized feedback, real-time analysis, and data-driven instruction.
Overall, technology has provided students with new learning opportunities and has made education more accessible, interactive, and personalized.
Learning topics:
There are many different topics that students can learn about using technology. Some examples include:
Mathematics: Students can use educational software, such as Khan Academy, to learn about a wide range of mathematical concepts, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus.
Science: Students can use online simulations, virtual labs, and interactive visualizations to learn about physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences.
Language: Students can use language-learning apps, such as Duolingo and Rosetta Stone, to learn new languages or improve their skills in a language they already know.
History: Students can use online resources, such as primary source documents and historical videos, to learn about historical events and figures.
Literature: Students can use e-books, online reading platforms, and interactive tools to explore literature and analyze texts.
Social Studies: Students can use interactive maps, videos, and virtual simulations to learn about geography, economics, government, and other social studies topics.
Programming: Students can use interactive coding platforms and tutorials, such as Codecademy and Scratch, to learn how to code and create their own programs.
Art and Music: Students can use digital tools to create, edit, and share their own art and music.
Overall, technology has provided students with a wide range of resources for learning about a wide variety of topics, making it easier for them to explore their interests and passions.
Student Topic:
The specific topic that a student may want to learn about using technology will depend on their interests and educational goals. However, some common areas of study that students may be interested in include:
Computer Science: Students can learn about programming, computer systems, and artificial intelligence.
Business and Economics: Students can learn about finance, marketing, and management.
Engineering: Students can learn about mechanical, electrical, and civil engineering.
Medicine and Biology: Students can learn about human anatomy, physiology, and genetics.
Environmental Science: Students can learn about ecology, sustainability, and natural resources.
Education: Students can learn about teaching strategies, classroom management, and curriculum design.
Humanities: Students can learn about literature, philosophy, and history.
Law and Political Science: Students can learn about legal systems, political theory, and public policy.
Art and Design: Students can learn about graphic design, fashion, architecture, and more.
Psychology: Students can learn about human behavior, cognitive processes, and neuroscience.
Overall, technology can provide students with a wide range of resources to learn about a wide variety of topics. Students should explore their interests and passions and find the resources that best suit their learning styles and goals.
Writing system:
A writing system is a method of representing language using symbols, letters, or characters. There are many different writing systems in use around the world, including:
Alphabetical writing systems: These systems use a set of letters to represent the sounds of a language. Examples include the Roman alphabet (used in English), the Greek alphabet, and the Arabic alphabet.
Syllabic writing systems: These systems use symbols or characters to represent syllables rather than individual sounds. Examples include the hiragana and katakana scripts used in Japanese and the Devanagari script used in Hindi.
Logographic writing systems: These systems use symbols or characters to represent words or concepts rather than sounds. Examples include Chinese characters (Hanzi) and hieroglyphics used in ancient Egypt.
Braille: This system uses a combination of raised dots to represent letters, numbers, and punctuation, which is used by visually impaired people.
Sign language: This system uses a combination of hand gestures and body movements to represent words and phrases, which is used by deaf people.
Technology has played a significant role in the development and spread of writing systems throughout history. Today, technologies such as computers and smartphones have made it possible for people to use and learn about different writing systems from all over the world. This has also helped to preserve and promote cultural heritage.
Paragraph - Topic:
Sentence - Linguistics:
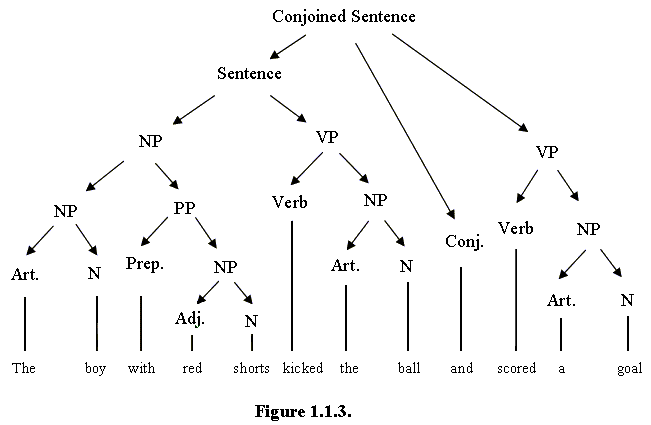
A sentence is a unit of language that expresses a complete thought or idea. In linguistics, sentences are studied as part of the field of syntax, which deals with the rules and principles that govern the structure of sentences in a particular language. Sentences can be categorized into different types, such as simple, compound, and complex, based on the number and type of clauses they contain.
Simple sentences contain only one independent clause and express a single idea or thought. For example, "The dog barked."
Compound sentences contain two or more independent clauses that are connected by a conjunction or a punctuation mark, such as a semicolon or a comma. For example, "The dog barked, but no one came to the door."
Complex sentences contain one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. The dependent clause provides additional information about the independent clause and is connected to it by a conjunction, such as "because," "when," or "although." For example, "The dog barked because it heard a noise."
In addition to analyzing sentence structure, linguists also study how sentences are formed in terms of their phonetics, phonology, morphology, and semantics. The sentence also has a pragmatic aspect, it can convey different meanings depending on the context and intonation, which is known as pragmatics.
For More Visit Us: SFreeSoftwares







.jpg)
0 Comments